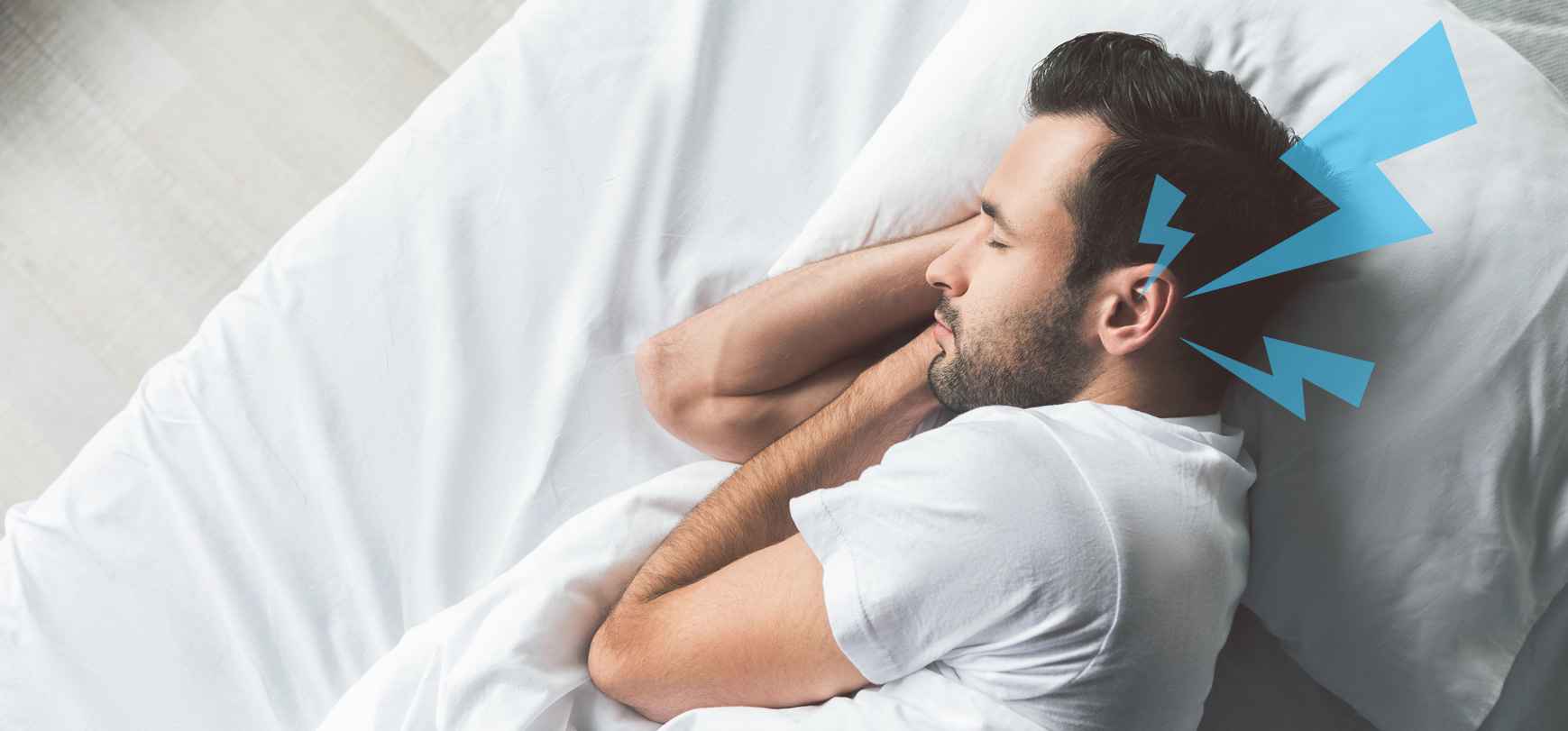
Tinnitus, the perception of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, can become especially troubling at night. When the world quiets down, and distractions fade, the sounds in your ears can feel louder and more persistent. However, there are ways to manage tinnitus at night, improve sleep quality, and minimize the effects of this condition. Here’s how to handle nighttime tinnitus and create a more peaceful, restful environment for sleep.
Understanding Nighttime Tinnitus
Tinnitus is often more noticeable at night due to the lack of external noise. During the day, sounds from your surroundings, such as traffic, conversations, or music, can mask the tinnitus. However, at night, with fewer external noises to compete with, the ringing or buzzing in the ears becomes more prominent.
Create a Calming Sleep Environment
One of the first steps in managing nighttime tinnitus is creating a peaceful sleep environment. Keep your bedroom as quiet as possible, and make sure it’s comfortable, cool, and dark. Consider using blackout curtains or an eye mask if light bothers you. The goal is to eliminate distractions that could worsen your tinnitus symptoms or make it harder for you to fall asleep.
Use White Noise or Sound Therapy
If the silence exacerbates your tinnitus, try using white noise or sound therapy. White noise machines, fans, or even smartphone apps can create a gentle, soothing sound that helps mask the ringing in your ears. Nature sounds, like rainfall or ocean waves, can also be helpful. These sounds don’t eliminate tinnitus, but they make it less noticeable and provide a distraction that promotes relaxation and sleep.
Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress and anxiety can make tinnitus symptoms worse, especially at night. Engaging in relaxation techniques before bed can help reduce stress levels and ease the mind. Consider deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation. These practices not only help manage tinnitus but also improve your overall sleep quality by promoting calmness.
Keep a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the effects of tinnitus. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. A consistent routine helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep and worsen tinnitus symptoms. Try to avoid these substances, particularly in the hours leading up to bedtime. Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake, while alcohol can lead to fragmented sleep and make tinnitus more noticeable.
Try Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment for managing tinnitus, particularly when it impacts sleep. CBT for tinnitus focuses on changing the negative thoughts and feelings associated with the condition. A therapist can help you develop coping strategies to reduce the stress, anxiety, and frustration that often accompany tinnitus, leading to better sleep and improved quality of life.
Seek Medical Advice if Necessary
If your tinnitus continues to disrupt your sleep and affects your quality of life, consider consulting with a healthcare provider. In some cases, underlying health conditions like hearing loss or ear infections may be contributing to your tinnitus. A doctor can help you identify the cause and recommend treatments to manage your symptoms.
Conclusion
Managing nighttime tinnitus can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can improve your sleep and reduce the impact of the condition. By creating a calming environment, using sound therapy, practicing relaxation techniques, and maintaining a consistent sleep routine, you can create a peaceful night of rest. If necessary, seek medical advice to find the best treatment for your tinnitus. With patience and the right approach, you can enjoy better sleep and less nighttime discomfort.






Be First to Comment